Emailing is one of the key communication methods, especially through B2C and B2B marketing and communication techniques. Phishing attempts can happen to anyone, so it is really important to be able to distinguish between a real and fake email.
What is phishing?
Phishing is a cyber-crime technique used to gain sensitive information such as usernames, passwords and card details. Cybercriminals use advanced methods to make an email seem authentic, such as making it look like it has been sent from a reputable sender. For instance, this could be the impersonation of a banking company. This makes it very easy for either you or your employees to believe and click on any provided links.
How to recognise a phishing email
There are key signs that can make it obvious that the email is just an attempt to gain sensitive information. Here are just a few of them…
Spelling mistakes
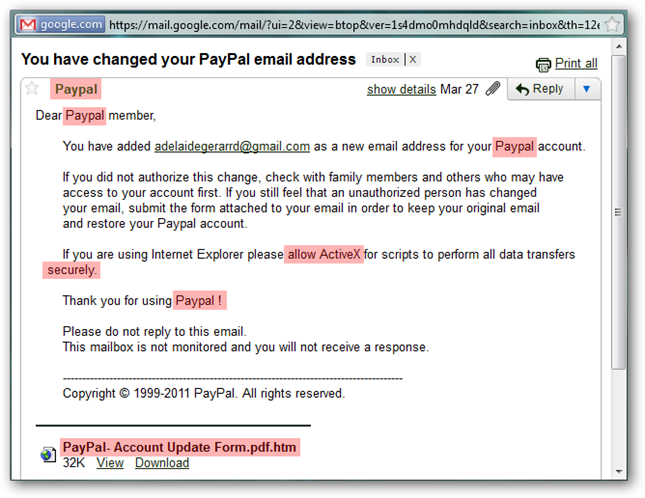
Often, emails from senders impersonating a company will contain spelling and grammatical mistakes that can help identify a scam. Double check the email for any mistakes, whether it be a missed apostrophe, misspell or punctuation error.
Notice in this example email from Jason Faulkner that there are many mistakes. One of the biggest indicators is the incorrect use of the name PayPal. This sender does not capitalise the second P.
Asking for sensitive information
As the sole purpose of phishing attempts is to obtain your sensitive information, the sender will be asking you to provide yours. This can be in the form of a link, download or asking you to reply to the email.
Many companies will let you know through their website or emails signatures that they would never ask you to provide any personal information over phone or email, so this is a way to know that it is a fake email. For example, this is included on the RBS website:
Unknown Sender
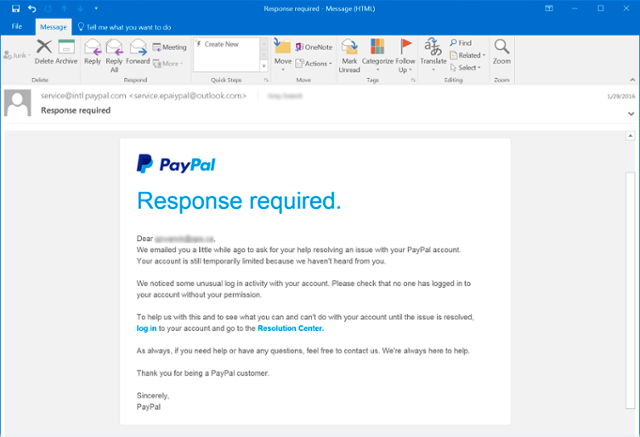
Some phishing attempts can come directly from a trusted company if they themselves have fallen into a trap, causing the email to also be sent to all of their contacts. Although in other attempts, it may be obvious if you carefully look at who the email is coming from.
If we examine this phishing email closely, you will see contained within angle brackets (<service.epaiypal@outlook.com>) the ‘real’ sender email address is displayed. This contains an email using an outlook domain name, which would never be used by PayPal.
Authentic Emails Will Be More Personal
Yes, your information can be sold to third parties, so in some instances, the phisher will know your email and your actual name. Although in other cases, they will not know or use your name in the email.
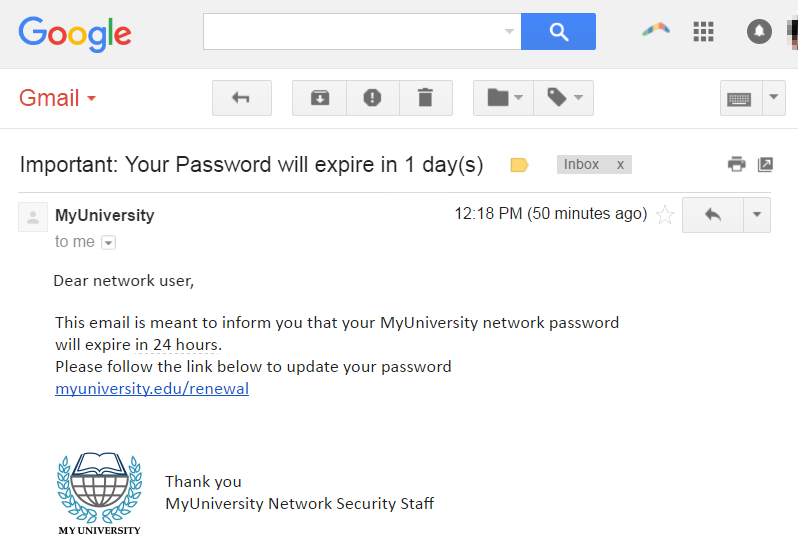
A business will usually use your name to identify you within an email, whereas a fake email will use a general term such as ‘Dear User’ or ‘Dear Customer’.
Still Unsure?
If you are still unsure, we recommend contacting the impersonated business directly. Make sure to use the contact details provided on their real website. They will be able to advise you on whether or not it is a phishing attempt. Just remember – in most cases, companies will never send an email requesting personal information.